The correlation between the structural design of dust removal skeleton and the extended service life of filter bags
Jan 15,2026
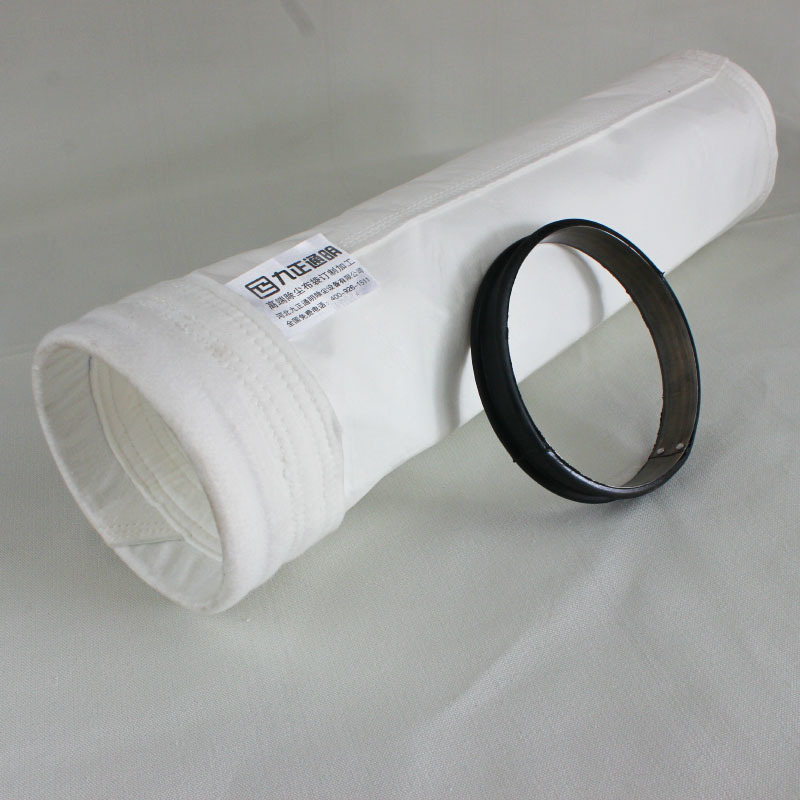

In industrial dust removal systems, the filter bag serves as the core filtering element, and its service life is directly related to dust removal efficiency, operating costs, and system stability. As the supporting component of the filter bag, the rationality of the structural design of the dust removal skeleton not only meets the basic function of "support", but also has a direct and critical impact on the stress state, wear degree, and air permeability efficiency of the filter bag, thereby determining the actual service life of the filter bag.
1、 Key structural design points of dust removal skeleton
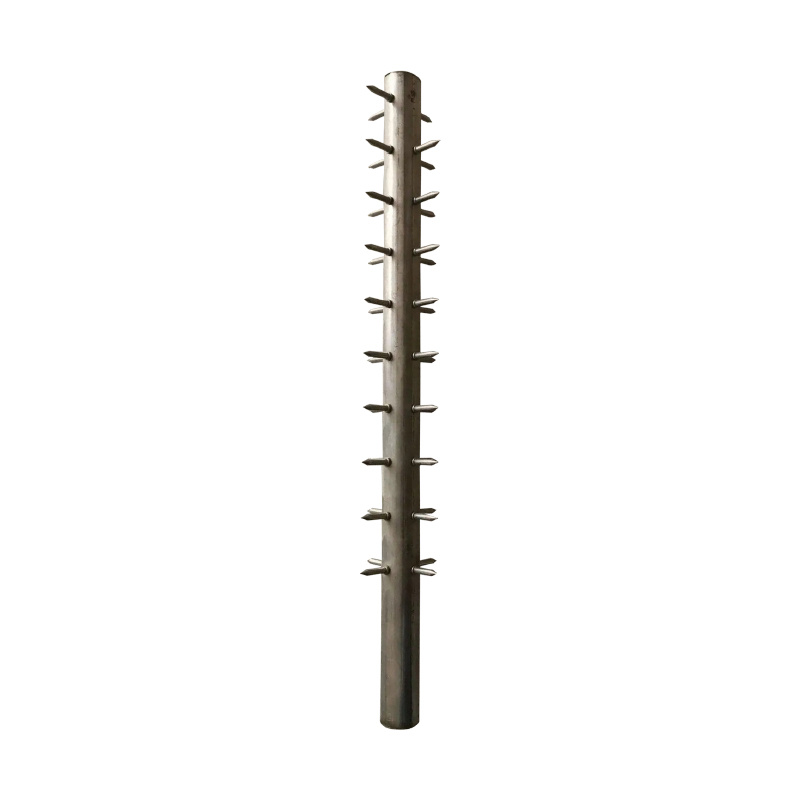
The dust removal framework is usually composed of longitudinal bars, support rings, Venturi tubes (if any), and upper and lower end covers. Its structural design needs to take into account multiple requirements such as support strength, compatibility with filter bags, and airflow circulation. The core design points mainly include: the overall dimensional accuracy of the skeleton, the arrangement of longitudinal bars and support rings, surface treatment technology, material selection, and end structure design. These design stages are interrelated and together constitute the key factors that affect the operation status of the filter bag.
2、 The specific impact mechanism of structural design on the service life of filter bags
(1) Overall dimensional accuracy: avoid "interference wear" and "loose dust accumulation" of filter bags
The matching accuracy between the outer diameter size of the dust removal skeleton and the inner diameter size of the filter bag is the primary factor affecting the service life of the filter bag. If the outer diameter of the skeleton is too large and forms an interference fit with the filter bag, the filter bag will be excessively stretched during the bagging process, causing damage to the fiber structure of the filter bag. At the same time, during the periodic operation of filtration and dust cleaning, there will be continuous compression friction between the filter bag and the skeleton, accelerating the wear of the fiber surface of the filter bag and ultimately causing damage to the filter bag. On the contrary, if the outer diameter of the skeleton is too small, there will be a large gap between the filter bag and the skeleton. The filter bag will shake violently under the action of airflow, which will not only cause uneven dust accumulation inside the filter bag and increase the difficulty of cleaning, but also cause concentrated wear at the local contact points between the filter bag and the skeleton; In addition, during the shaking process, the folds of the filter bag will suffer fatigue damage due to airflow impact and dust friction, which will also shorten the service life of the filter bag.
Therefore, a reasonable size design needs to ensure a "gap fit" between the skeleton and the filter bag, with a gap controlled within the range of 2-5mm (adjusted according to the material and working conditions of the filter bag), which not only avoids excessive stretching of the filter bag, but also prevents significant shaking of the filter bag, reducing physical damage to the filter bag from the basic level.
(2) Longitudinal reinforcement and support ring design: optimizing the stress and air permeability uniformity of the filter bag
1. Quantity and arrangement of longitudinal bars: As the main load-bearing component of the skeleton, the quantity and distribution density of longitudinal bars directly affect the support stability of the filter bag. If the number of longitudinal bars is too small, the filter bag is prone to local collapse under the filtering pressure. The filter bag in the collapsed area will not be thoroughly cleaned due to excessive dust accumulation. Long term dust accumulation will reduce the breathability of the filter bag, and the fibers in the collapsed area will fatigue and age due to continuous pressure; If there are too many longitudinal bars, it will increase the contact area between the skeleton and the filter bag, expand the range of friction and wear, and reduce the effective breathable space of the filter bag, affecting the filtration efficiency. Usually, according to the diameter of the filter bag, the number of longitudinal bars should be controlled between 8-24 and evenly distributed to ensure that all parts of the filter bag are evenly stressed and avoid local stress concentration.
2. Support ring spacing: The function of the support ring is to enhance the radial stiffness of the skeleton and prevent deformation of the skeleton. The spacing design should take into account both the support effect and the wear of the filter bag. The spacing between the support rings is too large, and the radial support strength of the skeleton is insufficient. Under the impact of airflow and cleaning pulse pressure, radial deformation is prone to occur, resulting in local compression and wear of the filter bag; The spacing is too small, although the support effect is good, it will increase the number of contact points between the support ring and the filter bag, increase the probability of wear, and increase the manufacturing cost of the skeleton. Practice has shown that when the spacing between support rings is controlled between 150-300mm, it can ensure the stability of the skeleton support and control the wear degree of the filter bag within a reasonable range. In addition, the shape of the support ring can also affect the wear situation. Compared to other irregular structures, the circular support ring has a smoother contact with the filter bag, which can reduce local wear.
(3) Surface treatment process: reduce the risk of friction damage and corrosion of filter bags
The surface state of the dust removal skeleton directly determines the friction coefficient between the filter bag and the skeleton when in contact, and also affects the corrosion resistance and high temperature resistance of the skeleton under harsh working conditions, thereby indirectly affecting the service life of the filter bag. If there are burrs, welding slag or high roughness on the surface of the skeleton, these protruding parts will scratch the fibers on the surface of the filter bag like a "blade" during the installation and operation of the filter bag. Especially during the expansion and contraction process of the filter bag during dust cleaning, the wear will further intensify; In addition, under conditions containing moisture and corrosive gases, the skeleton without effective surface treatment is prone to rusting. The oxide scale generated by rusting will fall off and adhere to the inner wall of the filter bag, not only scratching the filter bag, but also blocking the pores of the filter bag, resulting in filter bag failure.
The current mainstream skeleton surface treatment processes include galvanizing, spraying, anodizing, etc. The galvanizing process can improve the corrosion resistance of the skeleton and achieve good surface smoothness; The coating formed by the spray coating process has a uniform thickness, lower friction coefficient, and better corrosion resistance and high temperature resistance, making it suitable for more harsh working conditions; The anodizing process is mainly suitable for aluminum alloy skeletons, which can enhance their surface hardness and corrosion resistance. High quality surface treatment can make the surface roughness Ra of the skeleton ≤ 3.2 μ m, without any burrs or welding slag, fundamentally reducing the friction damage and corrosion risk of the filter bag.
(4) Material selection and end structure: Adapt to working conditions and avoid local stress concentration
1. Material selection: The material of the dust removal skeleton needs to be matched according to the working conditions of the dust removal system (temperature, humidity, corrosive gas concentration, etc.). Under normal temperature and non corrosive working conditions, ordinary carbon steel material can meet the requirements; In high temperature conditions (temperature>120 ℃), stainless steel material should be selected to avoid support failure of carbon steel skeleton due to high temperature deformation or strength reduction, which may cause uneven stress on the filter bag; In conditions containing corrosive gases or high humidity, materials with stronger corrosion resistance should be selected to prevent the skeleton from rusting and damaging the filter bag. Improper material selection can lead to a shortened lifespan of the skeleton itself, indirectly increasing the frequency of filter bag replacement.
2. End structure design: The upper and lower ends of the dust removal skeleton are key parts for the installation and stress of the filter bag, and their structural design needs to avoid local stress concentration. For example, if welding is used to connect the upper cover to the longitudinal reinforcement, it is necessary to ensure that the weld seam is flat and free of weld beads, otherwise it will scratch the mouth of the filter bag during installation; If the lower end is designed as a sharp structure, concentrated wear will form at the bottom of the filter bag. A reasonable end structure should adopt a smooth transition design, with the upper cover using a flanged structure and the lower end using a sealed or smooth support ring structure to reduce local stress and wear on the filter bag at the end, while facilitating the installation and disassembly of the filter bag.
3、 The core principle of optimizing the skeleton structure design and extending the service life of filter bags
Based on the above analysis, optimizing the design of the dust removal skeleton structure to extend the service life of the filter bag requires following the following core principles: firstly, the "compatibility principle" to ensure accurate matching between the skeleton size and the filter bag, avoiding interference or excessive clearance; The second principle is the "low wear principle", which reduces the friction coefficient between the skeleton and the filter bag by optimizing the arrangement of longitudinal bars, support rings, and surface treatment; The third principle is the "working condition adaptation principle", which selects the skeleton material and surface treatment process reasonably based on the temperature, humidity, corrosiveness and other working conditions of the dust removal system; The fourth principle is the "stress balance principle", which optimizes the end structure and connection method to avoid local stress concentration in the filter bag.
In practical applications, systematic optimization of the structural design of the dust removal skeleton can effectively reduce the physical wear, fatigue damage, and corrosion risks of filter bags, extend the service life of filter bags by 30% -50%, and improve the operational stability of the dust removal system, reducing overall operation and maintenance costs. Therefore, in the design and renovation process of the dust removal system, the importance of the dust removal skeleton as an "auxiliary component" should not be ignored. Its structural design should be coordinated with the selection of filter bags and working conditions to achieve efficient and stable operation of the system.
Hot Tags:
Contact Us
Tel:
WeChat:
WhatsApp:
E-mail:
Address:
338 National Road South, Longfengdian Village, Botou City, Hebei Province, China