Common faults of bag filter: practical guide from identification to solution
Dec 04,2025
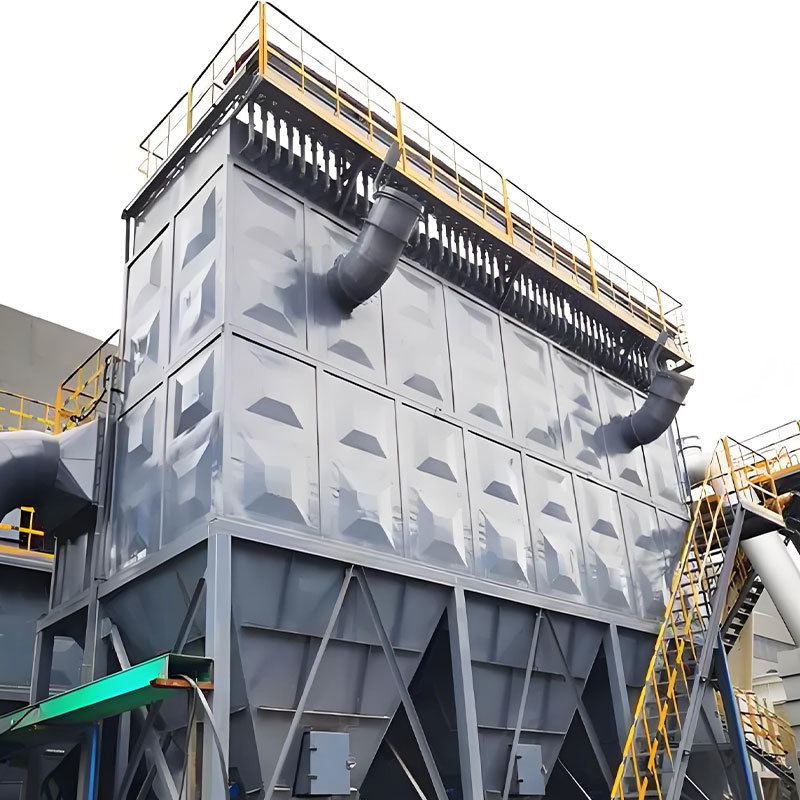

Bag filter has become the mainstream dust removal equipment in overseas industries such as chemical, metallurgical, and food due to its high filtration accuracy and wide adaptability to various working conditions. However, in long-term operation, due to fluctuations in working conditions, maintenance habits, and regional environment, it is easy to encounter faults such as filter bag damage and abnormal pressure difference, which not only lead to excessive emissions, but also may cause downtime losses, especially in areas with strict environmental regulations such as Europe and America. Failure to handle faults in a timely manner may result in high fines. This article summarizes 8 common faults of bag filter, disassembles the core causes and practical solutions for each fault, and adapts to the operation and maintenance needs of multiple overseas scenarios.
1、 Core fault of filter bag: the "hidden danger" of the filtration system
The filter bag is the "filtering barrier" of the bag filter, and its failure directly determines the operation effect of the equipment. It accounts for more than 60% of the total failures of the dust collector and needs to be prioritized and investigated.
1. Filter bag damage: a direct cause of excessive emissions
Phenomenon recognition: Visible dust overflow at the discharge outlet, and the dust concentration detector reading exceeds the standard; The pressure difference of the equipment decreased abnormally in the short term, but there was no significant rebound after cleaning.
Core causes: ① High dust cleaning pressure, pulse blowing force penetrates the filter bag; ② Filter bag aging and brittleness; ③ Skeleton burrs and weld beads scratch the filter bag; ④ Dust contains sharp particles and is subject to long-term erosion and wear.
Solution tip: ① Locate damaged filter bag: After stopping the machine, use a portable dust analyzer to detect each point at the filter bag mouth, or close the compartment valve to determine the damaged area through pressure difference changes; ② Emergency response: Small area damage can be temporarily repaired with high-temperature resistant tape, while large area damage needs to be replaced immediately; ③ Remedial measures: Adjust the dust cleaning pressure to 0.4-0.6MPa, check if the skeleton is smooth when replacing the filter bag, and use membrane wear-resistant filter material for sharp working conditions.
2. Filter bag blockage: the main reason for the surge in pressure difference
Phenomenon recognition: The pressure difference between the inlet and outlet of the equipment continues to exceed 1800Pa, causing an increase in fan current and a significant decrease in air volume; After cleaning, the pressure difference does not decrease significantly, and may even rebound.
Core causes: ① High humidity flue gas leads to dust adhesion, forming a "mud cake" that blocks the pores of the filter material; ② Incorrect selection of filter material; ③ The dust cleaning system is malfunctioning and the dust cannot be removed; ④ After shutdown, the filter bag became damp, and when restarted, dust formed.
Solution tip: ① Emergency handling: Open the equipment bypass valve, introduce 50-80 ℃ hot air into the filter bag chamber for drying, or manually shake the filter bag holder to remove dust; ② System optimization: Install a pre heater under high humidity conditions and replace it with membrane filter material or hydrophobic coating filter material; ③ Operation and maintenance adjustment: Shorten the cleaning interval, thoroughly clean the dust before shutdown, and avoid dust residue.
3. Filter bag aging: a hidden killer of shortened lifespan
Phenomenon recognition: The color of the filter bag darkens, the texture becomes brittle, and cracks appear with slight pulling; Frequent damage in the short term, with a replacement cycle of less than 6 months.
Core causes: ① Excessive high temperature; ② Smoke contains corrosive substances that erode filter fibers; ③ Excessive dust cleaning leads to damage to the fiber structure of the filter material; ④ In cold regions such as Northern Europe, filter bags are damaged by freeze-thaw cycles.
Solution tip: ① Detecting flue gas parameters: Use a thermocouple to measure the flue gas temperature and confirm whether it exceeds the tolerance value of the filter bag; ② Replace the suitable filter material: PTFE filter bags are used for high-temperature corrosion conditions, and low-temperature resistant filter materials are used for cold regions; ③ Optimize the dust cleaning program: dynamically adjust the dust cleaning frequency according to the dust concentration to avoid "excessive dust cleaning".
2、 Auxiliary system failure: "support hazard" in equipment operation
Malfunctions in auxiliary systems such as dust cleaning, unloading, and airflow distribution, although not directly involved in filtration, can indirectly cause damage to filter bags or a decrease in efficiency, and require simultaneous troubleshooting.
1. Pulse cleaning system failure: catalyst for filter bag failure
Phenomenon recognition: There is no obvious pulse blowing sound or weak blowing during dust cleaning; Filter bag blockage and damage alternate.
Core causes: ① Pulse valve diaphragm damage or aging; ② Compressed air contains oil and water, causing the solenoid valve to jam; ③ Pulse controller program disorder, injection timing error; ④ The spray pipe is offset and the nozzle is not aligned with the center of the filter bag.
Solution tip: ① Step by step troubleshooting: First check the compressed air pressure, then disassemble the pulse valve to check the diaphragm, and finally test the output signal of the control instrument; ② Component replacement: Replace the temperature and corrosion resistant membrane, install a dryer and oil mist separator in the compressed air pipeline; ③ Calibration adjustment: Adjust the position of the spray pipe to ensure that the deviation between the nozzle and the center of the filter bag is ≤ 5mm, and reset the control instrument parameters.
2. Ash unloading system blockage: the "source" of secondary dust
Phenomenon recognition: The ash level meter displays full range, the ash discharge valve makes a "stuck" abnormal noise, and even the motor trips; Dust accumulation occurs at the bottom of the equipment, causing secondary dust.
Core incentives: ① High humidity dust clumps and builds bridges in the ash hopper; ② The speed of the ash discharge valve is too fast or too slow, resulting in ash accumulation; ③ The smoothness of the inner wall of the ash hopper is insufficient, and dust adheres to it; ④ Dust freezes inside the ash hopper in extremely cold regions.
Solution tip: ① Emergency dredging: After stopping the machine, use an air cannon to break up the clumps, or gently poke open with a wooden stick manually. It is strictly prohibited to use open flames for baking; ② Structural optimization: Wear resistant and anti stick coating is laid on the inner wall of the ash hopper, and high-frequency vibrators are installed; ③ Regional adaptation: Install electric heat tracing on the ash hopper in cold regions, and install a rain cover on the top of the ash hopper in high humidity regions.
3. Uneven airflow distribution: the "driver" of local faults
Phenomenon recognition: Some filter bags in the same device are severely clogged, while others have little dust; The damage to the filter bag is concentrated on the air inlet side.
Core causes: ① The air inlet guide plate falls off or deforms, causing smoke to directly flush the local filter bag; ② Unreasonable air duct design and uneven distribution of wind speed; ③ Part of the filter bags were damaged and not replaced in a timely manner, resulting in a short circuit of the airflow.
Solution tip: ① Structural repair: Open the maintenance door, re fix or replace the guide plate, and install a uniform flow net at the air inlet; ② Operation adjustment: If the local filter bag load is too high, the corresponding compartment's dust cleaning system can be temporarily closed to reduce airflow impact; ③ Regular inspection: Check the guide plate and uniform flow net every quarter to avoid looseness or dust accumulation and blockage.
3、 Electrical and Control System Malfunctions: "Neural Problems" in Equipment Operation
Electrical system failures account for 20% of total dust collector failures and are often misdiagnosed as mechanical problems, requiring precise positioning through instrument detection.
1. Control instrument malfunction: the "core crux" of dust cleaning disorder
Phenomenon recognition: The cleaning timing is chaotic, and some pulse valves do not operate or continue to operate; The control panel is black and the buttons are unresponsive.
Core causes: ① Short circuit of power lines caused by high temperature and humidity; ② Program disorder or incorrect parameter settings; ③ Unstable power supply voltage; ④ The controller is aging and the components are malfunctioning.
Solution tip: ① Basic troubleshooting: Check the power supply voltage and use a multimeter to test the continuity of the circuit; ② Program recovery: Restore the controller to factory settings and reset parameters such as spray interval and width; ③ Environmental optimization: Move the controller to a sealed electrical cabinet, install a dehumidifier or voltage regulator, and adapt to harsh power supply environments.
2. Sensor malfunction: the "source" of parameter distortion
Phenomenon recognition: The reading of the differential pressure gauge does not match the actual reading, or fluctuates violently; The temperature sensor display is abnormal, causing the pre heater to malfunction.
Core causes: ① Dust accumulation and coverage of sensor probes; ② Sensors freeze in extremely cold regions; ③ Corrosive smoke corrodes sensor components; ④ Calibration expired, resulting in decreased accuracy.
Solution tip: ① Cleaning and calibration: Regularly blow the sensor probe with compressed air and calibrate it with standard instruments every quarter; ② Regional adaptation: Low temperature resistant sensors are selected for cold regions, and PTFE coated probes are used for corrosive conditions; ③ Redundant design: Key parameters can be equipped with dual sensors for cross validation of data accuracy.
4、 Special Reminder for Foreign Trade Scenarios: Key Points for Regional Fault Prevention
1. High humidity areas in Southeast Asia: The core faults are condensation on the filter bag and blockage of the ash hopper. It is necessary to install insulation layers and heat tracing devices on the equipment. The filter bag should be made of hydrophobic film, and the compressed air system should discharge liquid accumulation every week.
2. High temperature zone in the Middle East: Focus on preventing the aging of pulse valve membranes and high-temperature damage to filter bags. High temperature membranes resistant to 300 ℃ should be selected, and PPS or PTFE materials should be preferred for filter bags. Control instruments should be equipped with cooling fans.
3. European and American compliance zone: After troubleshooting, complete records must be saved. Some countries require data to be uploaded to the environmental protection platform, and it is necessary to ensure that the control system supports data export.
4. Remote areas in Africa: Faced with shortages of spare parts and unstable power supply, it is necessary to reserve vulnerable parts for three months and equip the electrical system with backup generators and voltage regulators.
5、 Fault prevention: Establish an "active operation and maintenance" mechanism
The cost of troubleshooting a bag filter is five times the cost of prevention, and establishing a standardized operation and maintenance mechanism can reduce the risk of failure by more than 60%
1. Daily inspection: Record parameters such as pressure difference, air volume, and cleaning frequency, and focus on checking whether the filter bag is damaged and the operation status of the ash discharge valve;
2. Weekly maintenance: clean the sensor probe, discharge accumulated water from the compressed air system, and check the operation of the pulse valve;
3. Monthly in-depth inspection: Open the equipment maintenance door to check the aging degree of the filter bag, the deformation of the skeleton, and the fixing status of the guide plate;
4. Quarterly calibration: Calibrate differential pressure gauges, temperature sensors, and controller parameters to ensure accurate data.
The core of troubleshooting bag filters lies in "first identifying the symptoms, then identifying the causes, and finally curing the problem", rather than blindly replacing components. Overseas operation and maintenance personnel need to combine local working conditions, be familiar with typical manifestations of various faults, and through precise judgment and system optimization, ensure stable operation of equipment while meeting environmental compliance requirements, providing reliable support for production continuity.
Hot Tags:
PREVIOUS:
Contact Us
Tel:
WeChat:
WhatsApp:
E-mail:
Address:
338 National Road South, Longfengdian Village, Botou City, Hebei Province, China