Practical tips for cleaning and extending the lifespan of electrodes in electrostatic precipitators
Dec 01,2025

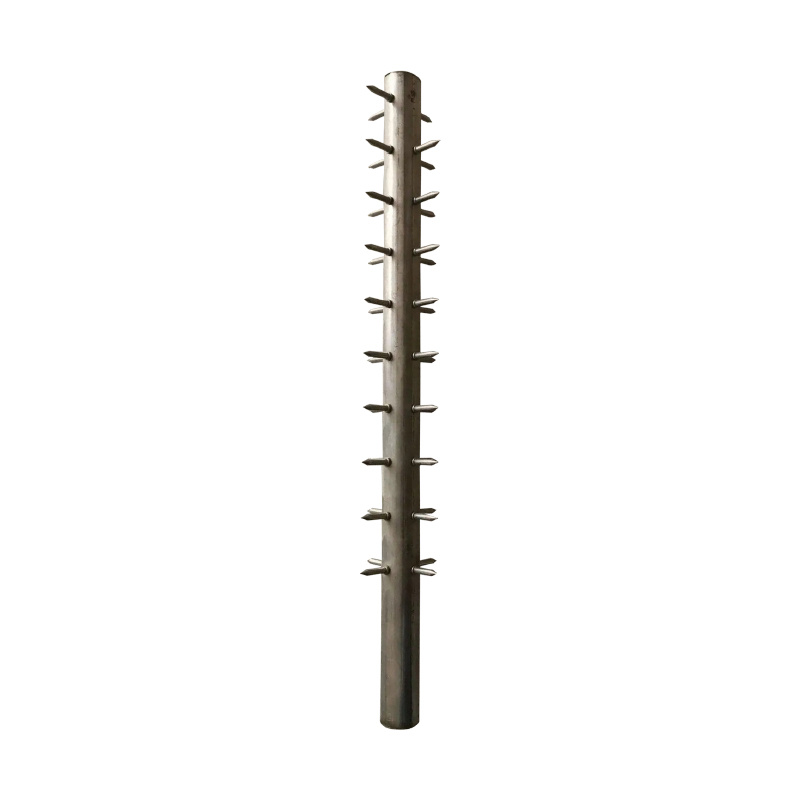
In industrial dust removal systems, the electrodes of electrostatic precipitators are the core working components, and their surface cleanliness directly affects the dust removal efficiency and equipment life. After long-term operation, dust, oil stains, and corrosive substances in the flue gas will deposit scabs on the electrode surface. If not cleaned in time, it can lead to a decrease in electric field breakdown voltage, an increase in energy consumption, and even cause electrode deformation, corrosion, and other faults. Especially in overseas high working condition industries such as chemical, metallurgical, and power, electrode pollution is more prominent.
1、 The core hazards and judgment criteria of electrode pollution
1. The direct impact of pollution
Pollutants on the electrode surface can disrupt the uniformity of the electric field, leading to a decrease in dust charging efficiency and an increase in emission concentration; The deposited hard blocks will increase the weight of the electrode, and long-term stress can easily cause cathode wire breakage and anode plate deformation; For corrosive flue gases containing sulfur and chlorine, pollutants combine with water vapor to form acidic electrolytes, accelerating electrode corrosion and, in severe cases, shortening electrode life by more than 50%.
2. Signal for immediate cleaning
The operating voltage of the electric field remains below 80% of the design value, or there are frequent occurrences of arcing and tripping;
The pressure difference between import and export has increased by more than 30% compared to the initial operating value, and the load on the fan has significantly increased;
Open the maintenance door and observe that dust clumps with a thickness exceeding 2mm appear on the electrode surface, or yellow brown or black corrosion spots appear;
The reading of the dust concentration detector at the emission outlet continues to exceed the standard, and after excluding other factors such as filter material and sealing, there is still no improvement.
2、 Scientific Method for Electrode Cleaning: Precise Selection by Pollution Type
Electrode cleaning should follow the principle of "determining the type of pollution first, and then selecting the cleaning method" to avoid blind operation that may cause electrode damage. Common cleaning methods include mechanical cleaning, high-pressure water cleaning, and chemical cleaning, which are suitable for different pollution scenarios.
1. Mechanical cleaning: suitable for dry and loose dust pollution
Applicable scenarios
It is mainly used to treat dry dust generated in industries such as cement and mining. The pollutants are mainly inert particles such as quartz sand and limestone powder, which are non viscous and non corrosive.
operation steps
Cut off the high-voltage power supply after shutdown, hang the "Do Not Close" sign, and wait for the electrodes to fully discharge (usually takes 15-30 minutes);
Wear protective equipment such as insulated gloves and dust masks, enter the electric field, and use nylon brushes and compressed air spray guns to blow and clean the anode plate and cathode wire;
For the fibrous dust wrapped around the cathode wire, gently peel it off with a specialized scraper to avoid pulling it forcefully and causing deformation of the cathode wire;
During the cleaning process, promptly discharge the fallen dust from the electric field to prevent secondary sedimentation.
Precautions
Do not use metal tools to directly strike the electrode to avoid deformation of the electrode plate and breakage of the cathode wire;
Compressed air needs to be dried and degreased to prevent water vapor and oil stains from adhering to the electrode surface and exacerbating pollution.
2. High pressure water cleaning: suitable for sticky, damp dust pollution
Applicable scenarios
Suitable for viscous dust in metallurgy, casting and other industries, or dust agglomeration caused by high humidity flue gas. The pollutants are mainly iron oxide, coke powder, etc., with certain adhesion.
operation steps
Clear the accumulated dust in the electric field in advance, lay waterproof cloth and water collection tank at the bottom of the equipment to prevent sewage leakage;
Select a high-pressure cleaning machine (pressure 8-15MPa, flow rate 50-80L/min), equipped with a fan-shaped nozzle, to uniformly flush from the top of the electric field downwards and from the inside of the anode plate outwards;
Washing sequence: Clean the anode plate first, then clean the cathode wire, with a focus on washing the edges of the electrode plate, the burrs on the cathode wire, and other areas that are prone to dust accumulation;
After cleaning, turn on the drainage device inside the electric field to completely discharge the sewage, and then use compressed air to blow the surface of the electrode to accelerate the evaporation of water.
Precautions
During flushing, it is necessary to maintain a distance of 30-50cm between the nozzle and the electrode to avoid direct impact of high-pressure water flow on the cathode wire, which may cause damage;
If the flue gas contains corrosive components, a neutral aqueous solution (pH 7-8) should be used for secondary flushing after cleaning to neutralize residual acidic substances;
Before the equipment resumes operation, it is necessary to ensure that the electrode surface is completely dry to avoid short circuits after power is applied.
3. Chemical cleaning: suitable for corrosive and stubborn pollution
Applicable scenarios
In response to stubborn pollution in industries such as chemical engineering and waste incineration, pollutants containing oil, sulfides, nitrogen oxides, etc. are difficult to remove using conventional cleaning methods and have formed corrosive crusts.
operation steps
Before cleaning, sample and analyze the pollutants on the surface of the electrode, select suitable chemical cleaning agents, and avoid using strong acidic or strong alkaline cleaning agents to corrode the electrode;
Dilute the cleaning agent proportionally (usually at a concentration of 5% -10%), spray it evenly on the electrode surface through a spray device, soak for 30-60 minutes, and allow the cleaning agent to fully penetrate and decompose pollutants;
Rinse the dissolved pollutants thoroughly with a high-pressure water cleaning machine, and then rinse repeatedly with clean water until the effluent is clear and has a neutral pH value;
After cleaning, dry the electrodes with compressed air or turn on the heating device inside the electric field (temperature controlled at 60-80 ℃) to accelerate drying.
Precautions
Operators need to wear professional protective equipment such as chemical protective clothing, goggles, and gas masks to avoid contact between cleaning agents and the skin and respiratory tract;
The cleaned wastewater needs to undergo neutralization and sedimentation treatment to meet local environmental discharge standards before being discharged, especially in compliance with strict environmental requirements in Europe, America, Japan, and South Korea;
The chemical cleaning cycle should not be too frequent, usually 1-2 times a year, to avoid long-term corrosion of electrodes by cleaning agents.
3、 Key techniques for extending electrode lifespan: comprehensive guarantee from operation and maintenance to selection
1. Optimize daily operation and maintenance: reduce electrode loss
Establish a regular inspection system: check the surface pollution of electrodes every week, measure the operating voltage and current parameters of the electric field every month, adjust the cleaning cycle in a timely manner according to the degree of pollution, and avoid long-term accumulation of pollutants;
Control the working conditions of flue gas: try to avoid high humidity and high corrosiveness flue gas directly entering the electric field. Pre processors can be installed at the inlet to reduce the corrosion of electrodes by flue gas;
Standardized start stop operation: Before starting the equipment, preheat the electric field to avoid power on operation in low temperature and humid environments; After shutdown, promptly clean the floating dust on the electrode surface to reduce the adhesion time of pollutants.
2. Strengthen electrode protection: enhance corrosion resistance and wear resistance
Surface treatment of anode plates and cathode wires, such as spraying anti-corrosion coatings, enhances the corrosion and wear resistance of electrodes, especially suitable for high corrosion conditions overseas;
Regularly check the tension of the cathode wire, and adjust it in a timely manner if there is any looseness to avoid collision between the cathode wire and the anode plate caused by vibration during operation, resulting in damage;
When replacing the electrode, choose a product that is compatible with the material: 316L stainless steel is used for high temperature conditions, and titanium alloy is used for corrosion conditions to ensure that the electrode matches the working conditions.
3. Optimize electric field design: reduce electrode workload
Adjust the wind speed of the electric field: control the wind speed at 1-1.5m/s to avoid excessive wind speed causing dust to wash over the electrode surface and accelerate wear;
Optimize power supply parameters: adopt intelligent high-voltage power supply, automatically adjust output voltage and current according to flue gas concentration, to avoid electrode overheating and corrosion caused by long-term high-voltage operation;
Regularly inspect the airflow distribution plate and guide plate inside the electric field to ensure even distribution of smoke and reduce local electrode overload pollution.
4、 Specially adapted to foreign trade scenarios: regional operation and maintenance adjustments
High corrosion areas: shorten the chemical cleaning cycle to once every 6-8 months, select electrode materials with stronger corrosion resistance, and install anti-corrosion lining inside the electric field;
High humidity areas: Emphasis should be placed on strengthening electrode drying treatment. After cleaning, a dual drying method of hot air drying and compressed air blowing should be used to avoid corrosion caused by long-term moisture on the electrode surface;
Cold regions: After cleaning in winter, it is necessary to thoroughly drain the accumulated water in the equipment, install insulation layers on the electrodes and pipelines to prevent freezing and damage to the electrodes;
Strict compliance requirements in regions: Chemical cleaning requires the use of cleaning agents that comply with REACH and EPA certifications. After cleaning wastewater treatment, testing reports must be retained for environmental audits.
The core of cleaning and extending the service life of electrostatic precipitator electrodes lies in "timely cleaning, scientific operation, and precise adaptation". By selecting appropriate cleaning methods, optimizing daily operation and maintenance processes, and adjusting protective measures based on regional conditions, it is possible to ensure stable operation of equipment, reduce emission risks, and effectively extend the service life of electrodes, thereby reducing the operation and maintenance costs of overseas factories. In practical operation, it is necessary to flexibly adjust the plan according to the equipment model and working conditions, and avoid blindly copying the standard process.
Hot Tags:
Contact Us
Tel:
WeChat:
WhatsApp:
E-mail:
Address:
338 National Road South, Longfengdian Village, Botou City, Hebei Province, China