Dust removal equipment operation and maintenance: a failure rate control method with prevention as the core
Nov 27,2025
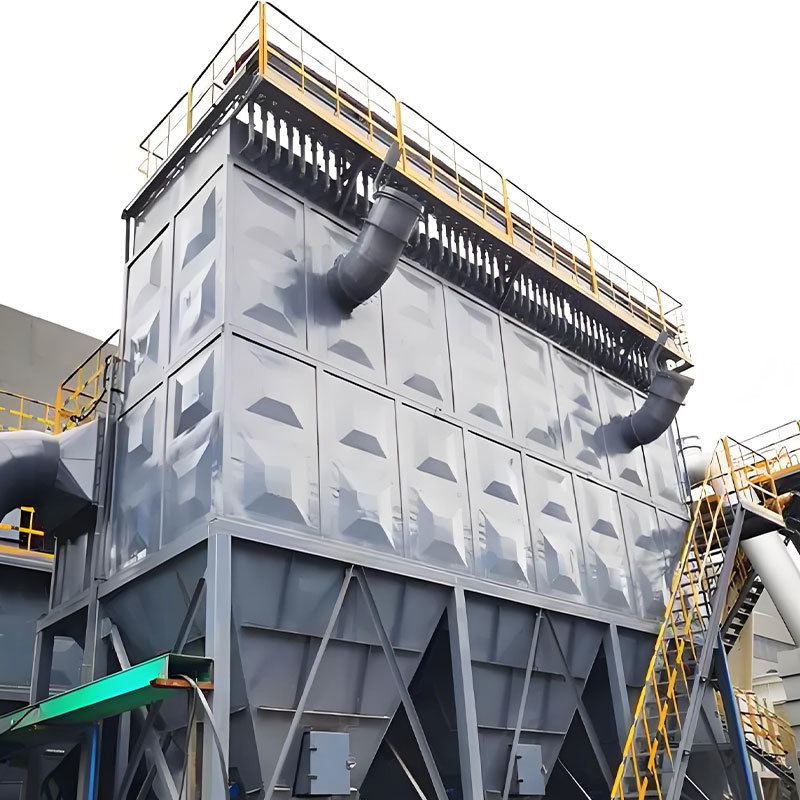

For overseas industrial factories, the stable operation of dust removal equipment is directly related to production continuity and environmental compliance. If the average annual failure frequency of a dust collector is reduced from 3-5 to less than 1, it can reduce at least 80% of downtime losses and maintenance costs. The core of reducing the failure rate is not "quick repair after failure", but establishing a "prevention oriented, precise operation and maintenance" system, scientifically managing equipment status, adapting to working conditions, and avoiding the causes of failures from the source.
1、 First, clarify the core: the three major root causes of dust removal equipment failures
All dust removal equipment failures can be traced back to three major categories of issues: human operation, component wear, and environmental adaptation. Operations and maintenance need to first identify risk points in a targeted manner:
Human error operation: accounting for 30% of the total number of failures, including failure to check parameters before starting up, incorrect setting of cleaning frequency, and non-standard replacement of filter materials. For example, reducing the pulse cleaning interval from 15 minutes to 3 minutes resulted in excessive wear of the filter bag.
Natural wear and tear of core components: accounting for 45%, vulnerable parts such as filter bags/cartridges, pulse valve membranes, electrode plates, etc. can shorten their lifespan by more than 50% under high temperature, high humidity, and corrosive conditions. If not replaced in a timely manner, it can easily lead to chain failures.
Mismatch between working conditions and equipment: accounting for 25%, such as corrosion caused by treating chemical acidic flue gas with ordinary carbon steel skeleton, or electrical short circuit caused by lack of moisture-proof treatment in high humidity areas. These faults are mostly due to insufficient adaptation in the early stage or lack of dynamic adjustment in operation and maintenance.
2、 Key operation and maintenance measures: from "daily inspection" to "system maintenance"
To reduce the failure rate, a closed-loop system of "high-frequency inspection precise maintenance intelligent warning" needs to be established, with different links focusing on core control points to avoid indiscriminate operation and maintenance.
1. Daily inspection: Avoid 80% of faults with 10% of the time
The core of inspection is to "look at parameters, check components, and listen for abnormal noises", and implement them in a graded manner of "daily weekly monthly" to form traceable records:
[Daily inspection (10 minutes/unit)] Core inspection items: pressure difference, fan current, emission concentration; Pulse valve blowing sound; Dust accumulation in the ash hopper. Abnormal judgment criteria: pressure difference>1800Pa or<600Pa; uneven blowing sound; The gray level gauge shows over 1/2.
[Weekly inspection (30 minutes/unit)] Core inspection items: Compressed air pressure; Appearance of filter bag/filter cartridge; Fan bearing temperature; Sealing element. Abnormal judgment criteria: pressure<0.4MPa; The filter material is damaged/bonded; Bearing temperature>70 ℃; Dust leakage at the sealed area.
[Monthly inspection (1 hour/unit)] Core inspection items: electrode plate nodules; Parameters of dust cleaning control instrument; Sensor calibration. Abnormal judgment criteria: electrode plate dust thickness>5mm; parameter drift exceeding 10%; The sensor error is greater than 5%.
Special reminder: Inspection records should include "date, inspector, abnormal situation, and handling measures". European and American factories can integrate with EHS systems to meet environmental audit traceability requirements.
2. Maintenance of core components: Customize replacement and maintenance cycles according to working conditions
The excessive replacement of vulnerable parts wastes costs, and delayed replacement leads to failures. It is necessary to clarify the maintenance cycle based on the working conditions to avoid a one size fits all approach
Filter bag/filter cartridge: In room temperature drying scenarios, polyester filter bags are replaced every 8-12 months; In high temperature scenarios, PPS filter bags should be replaced every 6-8 months; In high humidity and high viscosity scenarios, the waterproof membrane filter cartridge should be replaced within 3-5 months. When replacing, it is necessary to check whether the skeleton has burrs to avoid scratching the filter material.
Pulse valve and diaphragm: The service life of industrial grade pulse valve diaphragm is about 1 million times of spraying. It is recommended to disassemble and inspect it every 6 months. If cracks or decreased elasticity occur, replace it immediately; The compressed air pipeline needs to be drained and oil drained weekly to avoid impurities blocking the nozzle.
Electrode and insulation components: Clean the dust and nodules on the electrode plate with a soft bristled brush every month to avoid uneven electric field; Insulated porcelain bottles need to be kept clean, and heating sleeves should be installed in low-temperature areas to prevent insulation failure caused by condensation.
Fan and bearings: Add lubricating oil suitable for the working conditions every week (320 extreme pressure oil for high temperature and 46 mechanical oil for normal temperature), and keep the oil level at 1/2-2/3 of the oil level mark; Check the tension of the belt every quarter and adjust it promptly when it becomes loose.
3. Optimization of Dust Cleaning System: Balancing Efficiency and Component Loss
The dust cleaning system is a high-risk area for malfunctions. Excessive dust cleaning can accelerate the wear of filter materials, while insufficient dust cleaning can lead to blockage. It needs to be dynamically adjusted according to the characteristics of dust:
Bag/filter cartridge dust collector: When the dust concentration is high, the cleaning interval is 5-8 minutes, and the spraying pressure is 0.4-0.5MPa; When the concentration is low, interval 15-20 minutes and pressure 0.3-0.4MPa. Avoid using high pressure to forcibly clean dust.
Electrostatic precipitator: For high humidity dust, the cleaning frequency should be increased to prevent dust from adhering to the electrode; Low specific resistance dust can reduce the frequency of dust cleaning and minimize electrode wear.
Cyclone dust collector: When the dust accumulation in the ash hopper reaches 1/3, it must be cleaned. High viscosity dust needs to be accompanied by a high-frequency vibrator to avoid clumping and bridging, which may cause equipment overload.
4. Intelligent warning: Capturing fault signals in advance with data
Traditional operations and maintenance rely on manual experience, while intelligent monitoring can provide fault warnings 2-3 days in advance, making it particularly suitable for remote management of overseas factories
Required monitoring modules: dust concentration sensor, differential pressure transmitter, temperature sensor, data threshold can be set according to local standards (such as EU emissions ≤ 10mg/m ³).
Linkage control logic: When the pressure difference is greater than 1600Pa, the system automatically shortens the cleaning interval; When the temperature exceeds the upper limit of the filter material's tolerance, trigger a cooling or shutdown warning; When the sensor data is abnormal, it will be pushed to the operation and maintenance personnel through SMS/email.
3、 Adaptation to Foreign Trade Scenarios: Dealing with Challenges in Different Regional Working Conditions
The temperature, humidity, and dust characteristics vary greatly in different regions overseas, and operation and maintenance need to be adjusted accordingly to avoid faults caused by "unsuitable water and soil":
High temperature and high dust areas in the Middle East: The core risks are motor overheating and filter material aging. Key points of operation and maintenance: Clean the fan cooling fins every week and install cooling fans in the electrical cabinet; Select high temperature resistant filter bags and check the integrity of the filter material coating every month.
High humidity areas in Southeast Asia: The core risks are equipment corrosion and filter material adhesion. Operation and maintenance focus: Spray anti rust paint on carbon steel skeleton and shell every month; Install heating device on the ash hopper; After cleaning, use compressed air to blow away moisture on the surface of the filter material.
European and American compliance zone: The core requirements are data traceability and component compliance. Operation and maintenance focus: Save the CE/FDA certification documents for each batch of filter materials; Synchronize inspection records to the factory MES system for easy auditing by EPA or EcoVadis; Fault repair requires the use of compliant accessories.
Remote areas in Africa: The core pain points are shortage of accessories and lagging technical support. Operation and maintenance focus: Reserve vulnerable parts for 3-6 months of usage; Choose devices with simple structures; Regularly conduct training for local operation and maintenance personnel.
4、 Common operational misconceptions: avoid the pitfall of "the more you maintain, the easier it gets to break down"
Some operation and maintenance operations may seem reasonable, but they can actually accelerate equipment wear and tear. It is important to focus on avoiding:
Misconception 1: Using cheap accessories to reduce costs: For example, replacing high-temperature resistant silicone pads with ordinary rubber pads can save money in the short term, but it is prone to aging and air leakage within 3 months, causing abnormal pressure difference. Correct approach: Select compliant accessories according to the working conditions, such as ATEX certified pulse valves for explosion-proof scenarios.
Misconception 2: After the filter material is damaged, "filling holes" and continuing to use it: Temporary filling holes can cause airflow short circuits, increase the load in undamaged areas, and accelerate overall failure. Correct approach: If any damage is found, immediately replace it individually to avoid bulk damage.
Misconception 3: Neglecting cleaning after shutdown: Failure to clean the filter material dust before long-term shutdown can cause clumping in high humidity environments, leading to a sudden increase in resistance during the next startup. Correct approach: Before stopping the machine, trigger a comprehensive ash cleaning, empty the ash hopper, and if necessary, cover the equipment with plastic sheeting.
Misconception 4: Failure to calibrate sensors: Long term failure to calibrate sensors can lead to data distortion, such as dust concentration display meeting standards but actually exceeding them, or false pressure difference leading to ineffective dust cleaning. Correct practice: Calibrate the concentration sensor with standard gas every month and calibrate the differential pressure gauge every quarter.
5、 Summary: Operations and maintenance are "cost reducing investments" rather than "additional costs"
The operation and maintenance cost of dust removal equipment usually accounts for only 5% -8% of the total equipment price, but it can determine 80% of the equipment's service life and operational stability. For overseas factories, a scientific operation and maintenance system can not only reduce the failure rate to less than once per year, but also extend the equipment life by more than 30%, reducing environmental fines and downtime losses caused by failures. The core logic is always "prevention first", which captures anomalies through high-frequency inspections, customizes maintenance plans according to working conditions, and uses intelligent data to assist decision-making, transforming dust removal equipment from "passive maintenance" to "active health management" and becoming a stable guarantee for the production process.
Hot Tags:
Contact Us
Tel:
WeChat:
WhatsApp:
E-mail:
Address:
338 National Road South, Longfengdian Village, Botou City, Hebei Province, China